Onderzoeksmethoden 2/het werk/2012-13/Group 2/Archive
Inhoud
- 1 December holiday gift-receiver associations with students in Nijmegen.
- 1.1 Is it possible to create a questionnaire that asks students in Nijmegen what gifts they buy for whom during which holiday in December?
- 1.1.1 Introduction
- 1.1.2 Practical use
- 1.1.3 Concept
- 1.1.4 Method
- 1.1.4.1 Possible directions
- 1.1.4.2 Chosen focus
- 1.1.4.3 Interview
- 1.1.4.3.1 Questions
- 1.1.4.3.1.1 Question 1
- 1.1.4.3.1.2 = Question 1a =
- 1.1.4.3.1.3 Question 2
- 1.1.4.3.1.4 Question 3
- 1.1.4.3.1.5 == 3a What do you think is a good gift for X? =
- 1.1.4.3.1.6 = 3b. How many presents do you give to this person? =
- 1.1.4.3.1.7 == 3c. Would you buy gifts for X together with others? (Who?) =
- 1.1.4.3.1.8 == 3d. How do you come up with the idea of what to buy for X? =
- 1.1.4.3.1.9 == 3e. Do you have a specific budget for buying gifts for X? =
- 1.1.4.3.1.10 == 3f. Where would you usually buy gifts for X? =
- 1.1.4.3.1.11 == 3g. When do you usually buy gifts for X? =
- 1.1.4.3.1.12 == 3h. Do also receive gifts from X? =
- 1.1.4.3.2 = 4 For which December holiday would you give X a present usually?
- 1.1.4.3.3 Processing
- 1.1.4.3.1 Questions
- 1.2 Transcription
- 1.1 Is it possible to create a questionnaire that asks students in Nijmegen what gifts they buy for whom during which holiday in December?
December holiday gift-receiver associations with students in Nijmegen.
//TODO: Go through text and replace buying with something about associating.
Is it possible to create a questionnaire that asks students in Nijmegen what gifts they buy for whom during which holiday in December?
Introduction
We want to find out what kinds of gifrst students in Nijmegen associate with which people in their lives during the holiday period in December. We'd like to create a questionnaire that asks students this so that we can identify their possible buying behaviour for these holidays.
Erik: include a ORM model to highlight the parameters that are involved in your research.
Why 'students in Nijmegen'?
We assume that each category of people who give gifts has its own properties.
For example students and grandparents have different budgets, interests and knowledge. To create a questionnaire that covers every consumer group everywhere is unrealistic because of these different properties. We therefore chose to limit our focus to students.
The reason for focusing on the Netherlands is that we also think that what people give depends on cultural backgrounds. The types of holidays will also differ.
The reason for choosing students in Nijmegen specifically, is partially practical, from an availability standpoint. We have more access to this target audience than to others, which will make our research easier. We cannot however make assumptions based on students in Nijmegen about students, in for example, Amsterdam. Therefore we will only focus on Nijmegen. Other researchers might want to expand on this research and look at more/other groups in Nijmegen, or other places. Comparisons with our results could also be made with students from other countries.
Why are we interested in the different groups of gift receivers?
We also assume that different groups of receivers, receive different gifts. We for example would buy different presents for our grandparents than for our little siblings. We want to research if there is a difference in what our target audience buys for different people in their lives. It might be possible that some people never give gifts to some relationship types.
Our research could show that some groups are very likely to receive gifts of a certain nature, this opens opportunities for more research on these and the reasons why.
//TODO : find research on gift receiving, gift targets, etc.
Erik: NB there is no need to do any serious literature review to find such research!
Why are we focusing on the December holidays?
There are a huge amount of holidays in the world throughout the year. We think that different presents are given for different holidays. So in order to create a questionnaire that is useful will become hard if there is a too big set of possible gifts, dates, etc.
Since we are focussing on students in the Netherlands we have decided to focus in December holidays. XYZ research shows that these are the most important holidays for most people. We know that in the Netherlands there are two celebrated holidays in December, namely: 'Sinterklaas' and 'Christmass'. Our study might give some interesting insights in the gift buying behaviour of people here depending on the holiday.
ABC research also shows that December is an important month for retailers. This means that the results of our questionnaire might provide opportunities for retailers to gain knowledge about, in this case, students and their gift buying behaviour.
//TODO: List of different holidays in different countries throughout the year.
//TODO: Find research/articles on Dutch holidays
//TODO: Find research/articles on present types depending on holidays, etc
Erik: NB Again, there is no need to do any serious literature review to find such research! Of course, you could do a quick search but only to find some helpful raw data eg. about which hoilidays there are.
Erik: You will have to come up with classifications/categorisations for the parameters in your research, such as present types, friend/relation types,holidays, etc. Note that here you have a choice for each parameter to make an (initial) classification before you do your interviews - which you then may have to tweak afterwards, or only doing this afterwards and extract it from the interviews.
Practical use
As mentioned before, the results of our research could be used for different purposes. The most important would be in advertisement and marketing. Targeted advertisement can be performed during the holiday period.
Christmass gift boxes that employers give to employees are often put together at specialised companies. Our research could provide them with insights on what people like to give to each other, thus what employers might want to give to their employees.
Another example would be financial advice related to budget advice for certain groups, in this case students. Advisors can help students plan for the extra expenses related to holiday gift purchases.
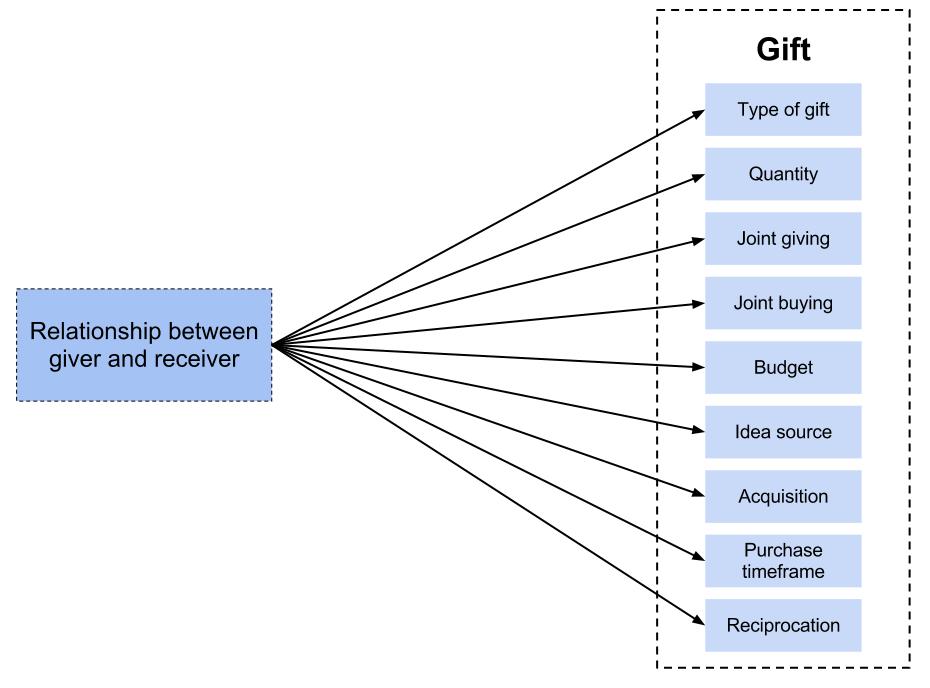
Concept
We will measure the influence of the relationship that the giver has with the receiver on our variables:
- Type of gift
- Quantity: How many gifts does the giver buy for the receiver?
- Joined giving: Is the receiver group of 2 or more people? Who?
- Joined buying: Does the giver buy a gift for the receiver together with someone else? Who?
- Budget
- Idea source: Where does the giver get the idea of what kind of presents to give the receiver?
- Acquisition: Where does the giver buy the gift(s) for the receiver?
- Purchasing time frame: When does the giver buy the gift(s)?
- Reciprocation: Does the receiver also give a present back to the giver?
Erik: joined <- joint
Erik: I guess the bottom arrow in your diagram is the "gift giving" relationship, and eg gift is an attribute of that relationship rather than the "relationship" relationship.
Classification
Simple
There are a few simple variable classifications.
- Reciprocation: yes/no
- Quantity: A number. After the interview we'll be able to determine appropriate ranges.
- Joined buying: yes/no
- Who? This will follow the classification of relationship type.
- Budget: A budget range in euros. After the interview we'll be able to determine appropriate ranges.
- Purchasing time frame: A time-range.
- Relationship type: A list of relationship type. For example: "Mother", "Father", "Brother", "Friend", "Partner", "Child", "Wife", etc.
- Joined giving: yes/no
- Who? This will follow the classification of relationship type.
Complex
- Type of gift:
- Acquisition:
- Idea source:
Method
Possible directions
There are a number of directions in which we can go with the eventual questionnaire. We can have a questionnaire that is purely meant to make an inventory of what categories of product are popular for which relationship type. We can however also expand this:
- Where do you buy presents?
- Do you use online stores?
- When do you buy your presents?
- What kind of budget do you have for presents?
- Do you save up for buying gifts?
- How does the recipient influence your budget allowance?
- Why do you buy certain presents?
- Do you buy what you'd like to receive, or what the receiver would like?
etc
Chosen focus
// TODO: Write something about why we chose to focus on the less psychological factors
Interview
Questions
We will collect the following data from our interviewee:
- Age
- Gender
- Education (?)
- Nationality
Question 1
We will ask the interviewee to write down on post-its the names or titles (e.g. 'Father' , 'Mother', 'Little brother', 'Grandma & Grandpa') that he/she would/could buy presents for during the december holidays.
= Question 1a =
Do you give one or more presents to any of these people together?
Question 2
We will ask the interviewee to sort these people based on their own vision of importance.
Achilleas: Maybe we should select randomly? Erik?
Question 3
We will select the first x of these gift receivers and ask the following questions about each (X) of them.
== 3a What do you think is a good gift for X? =
Result: list of gifts that would be suitable for X.
If they already bought something at interview-time: "What else did you think about buying for X?"
= 3b. How many presents do you give to this person? =
== 3c. Would you buy gifts for X together with others? (Who?) =
== 3d. How do you come up with the idea of what to buy for X? =
Result: Different idea sources.
== 3e. Do you have a specific budget for buying gifts for X? =
Result: Price range
== 3f. Where would you usually buy gifts for X? =
Results:
- Physical:
- Shopping center/mall
- Small detail stores
- etc
- Internet:
- Do you have specific websites that you go to to buy gifts for X?
- Google?
== 3g. When do you usually buy gifts for X? =
Result: General range (e.g. jan-aug, sept-nov, december, week before, day before
== 3h. Do also receive gifts from X? =
Result: yes/no
= 4 For which December holiday would you give X a present usually?
Result: ['Sinterklaas', 'Christmass', etc]
Processing
We will transcribe these interviews and then do a content analysis on the interviews in order to be able to determine associations that students in Nijmegen have with gifts they give to certain people in their lives.