Capita selecta Informatiekunde/student contributions/GebruiksvriendelijkeSystemen
Inhoud
- 1 Target Group
- 2 My contribution
- 3 Lead
- 4 Article
- 5 Introduction
- 6 Human Computer Interaction
- 7 Systems related
- 8 Improvement of usability
- 9 Existing systems
- 10 Future Work
- 11 Used articles
- 12 References
Target Group
This article is for people that make daily use of the Internet and services on the Internet.
My contribution
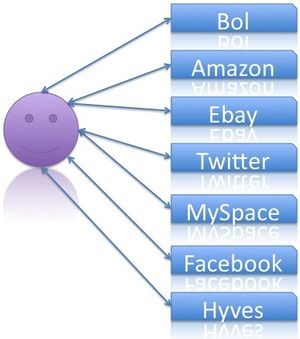
The contribution to this problem from my side is that I want to look for a solution to solve this usability issue that raised in the past years. A lot of web pages have been developed and many of them require user name and password. Users get annoyed of logging on and logging off. Portals like Ebay and Amazon make it possible to receive different offers from different sellers. At Ebay you only need one account and you can buy from every seller registered at Ebay. It is even possible to log on on other ebay systems like US, GB, or other countries. The same situation is present at Amazon where you can buy from Amazon directly or from sellers registered at Amazon. Systems like Ebay and Amazon show that centralization is possible. In addition to that systems like Twitter, MySpace, Facebook, etc. can be connected to each other. A post on twitter can be directly posted on Facebook and MySpace. Furthermore all Twitter-posts can be shown via a plugin on any webpage you like. Via this plugin interconnectivity is made possible. A lot of users want to connect the systems and simplify the usage of log on information. Unskilled users tend to use same passwords and user names because they cannot save several passwords. If users could trust a single system they would only have to remember one password and user name. The single system would simplify the usage of a lot of services. The services would also gain from the central system because users can either choose to use the system with or without the central system. If the service is used in the central system there will be more competition.
Lead
Many internet users have a lot of accounts on the internet: Facebook, Ebay, Amazon, Twitter, everything needs user name and password. Imagine you had one account and could use all your favorite services with one user name and one password. That would be something you remember, wouldn't you?
Article
What was my password again? That is one question many Internet users daily have. Internet users have accounts at so many systems that they lost overview of all the systems where they are registered. Browsers nowadays offer the possibility to save passwords for the users - to improve usability. The passwords are stored on the local computer. If the users surf via another computer or via their mobile phone / pda they have to remember the password, because the computer does not know it. Wouldn't it be nice when the computer would know all the passwords? It would be an advantage for the user if he only had one single password and user name. A solution could be that the user always uses the same password and user name, but that would not be possible because different system require different complexities of passwords. In addition to that also the user names have different structures at different systems. In the one system the user himself can choose the user name and in another system the user name is the email address of the user. In addition to that the accounts will be vulnerable. When users have the same user name and password different systems could use this information to exploit information on other services, where the user is registered. Nobody wants this situation but it is actually present everywhere where fingerprints are used. The fingerprint of person does not change, when he uses another system. In principal these systems are very vulnerable since a copy of fingerprints is no problem anymore. Look at your own laptop: do you have a fingerprint scanner?At the Radboud University students are working on a central approach where the user will have one account. Via this single account the user will be able to gain access to almost all his favorite Internet services. The central system will allow the user to register all his favorite services and if the user logs on he gains access to those systems. The advantage is obvious: the user only needs to remember one password. Even more the user is able using several services by remembering only one single password and user name. The central approach makes it possible that in the central system the user information is saved. Once this information changes all connected services will get an update of the user information. As result the user would have to change his address for example once, but it is updated on all connected services.
The system should be secured via secure connections to the different services like Amazon, Ebay, Twitter, etc.. In addition to that the students of the Radboud University think about a solution where buying a product can be directly send to the social networks like Twitter. Everyone will be notified about the purchase of the product. The central system will connect all services where the user is registered. This will improve the usability for the user and when he is looking for a new product he can start searching for product in different stores at the same time, like Ebay and Amazon. So he will be able to get the best price and conditions for the product he is searching. In the social networks users would be able to upload their photos once and the photos would be spread to all connected social networks. Furthermore users are able to search for people in different networks at the same time. The same will count for groups where many users participate. All this functionality would be realized through a single interface and users will not have to accustom to use several services, but accustom to use one single central service. This service wide implementation would simplify the information flow in the internet. Information would be spread through several services at the same time.
Just like Google, Facebook, etc. where users can watch/upload videos, read email, have photo albums and use small gadgets from the central service would offer so much functionality and connect several services. Looking at others trends in the information technology sector the aim is centralization again. Just like in the 70s central server were used and users just connected to the server via a terminal. Users only had a monitor and a keyboard, later also a mouse. With a small device which connected to the server everyone worked on the central server. In the past few years there was also a new trend where every service was outsourced to the Internet. So that everyone with a browser is able to use the same service, with the same front-end and the same database.Today there is a new trend called Cloud Computing where services are offered via Internet and users gain access to the services via their browser. Cloud Computing is also a central solution which only requires a browser on the computer/device. Everything lies on the server and can be accessed via browsers.
Introduction
When computer users are asked about their experiences with new software and hardware they mostly talk about the usability. They mention how quick they could reach a certain goal and how easy or difficult it was to fulfill the task thast was asked of them. The focus of software development has moved the previous years from functionality to usability. The reason therefore is that the users have the tendency to fasten switch from unusable software to software with less functionality. As [1] shows that human processing theory has become a part of software development, for a better software development.
Next to software development also the development of websites changed in the previous years. The possibilities of the internet increased dramatically and some developers have the tendency to set up an operating system which only connects the users with the Internet. [2] This trend shows that the development of websites will have to take usability into account. The issues of usability at websites are on the one side the compatibility with any browser software, but on the other site also the arrangement of buttons, texts, links and images. When a browser is not supported by a website the user will have problems of using the website and gain the information he wants. The arrangement of the elements on a page are the most important factor of the user's overview of the website.
Many users tend to use alternatives to the normal PC, like PDAs, SmartPhones, Notebooks and a lot of other forms. Mostly the hardware is different and also has some usability. Some devices may have a lot of buttons and others use a variable touch screen. The touch screen makes it possible that buttons get different meanings, colours and styles. Fixed hardware buttons are simple and the users just has to save the functionality of the button once. Since the prices of electronic devices dropped devices are installed everywhere: in the kitchen, in the bathroom, in the bedroom, in the living room (radio, tv, dvd player, satellite receiver) and even in the car (car stereo, navigation, handsfree-set). There is not nearly any building left where no electronic device is installed. Every device with a button can be analyzed in the means of usability.
Human Computer Interaction
Today it is question how usable a website or system is to be successful. Websites that are easier to use get a better performance grade than other websites. But the usability, what is it actually? In the first part some definition was cited but not very satisfying and looking at [3] there is something more specific. Palmer (2002) talks about 5 crucial elements for usability: consistency of interface, response time, mapping and metaphors, interaction styles and multimedia.
The consistency is the first item on the list of Palmer (2002) and later he is more specific about navigation tools, arrangement of elements, buttons and bars. A log on procedure can be seen as a part of the navigation. The navigation is the most important element of usability because users want to seek for information and if the information is protected they have to authenticate themselves.
This leads to the assumption that also password authentication or log on procedures can be seen as part of usability. The usability will be responsible for success of a website or program.
Before an analysis of usability can be started, first the term 'usability' has to be defined. A definition found on [4] states that a human has to be able to archive a certain goal with a certain tool. Even an ISO standard has got a definition for it like ISO 9241-11: "The extent to which a product can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction in a specified context of use." [5]
Usability plays a major role at every electronic system. Electronic systems mostly are based on certain software that runs on a certain hardware. For example a car radio has certain physical buttons, but there is also a software that reacts on the buttons. The same counts for smart phones with touch screen. Most of these smart phones have physical buttons like power switch and volume up/down. Depending on the chosen model more buttons are available. The touch screen makes it possible that buttons can be variable. The function of buttons can differ, but not just the place, but also size, place, color and shape. The touch screen is completely defined by the software inside the device. The software also will define the layout of text, buttons, images and at all arrangement of elements. The arrangement is one of the most common used measurements for usability.
The same approach can be applied to website where users are confronted with an arrangement of text, buttons and images. Next to this the usability of a website also depends on the browser used by the website visitor. Niche users like linux and mac users are might run into problems when a website is optimized for a certain version of a windows browser.
In the most cases when users are confronted with an electronic device like cell phones, pdas, notebooks or computers they have to identify themselves using login name and password. This procedure is almost 50 years old [6] and a basic way for computer security. The user name will authenticate the user and the password will verify that it is the user himself, assuming he is the only one knowing the password. When the system has recognized the user, he certain user rights will be assigned to the user so he will be authorized.
Some systems like newer operating systems expect a complex password meaning the password should contain certain kinds of characters like symbols, numbers and upper- and lowercase letters. Users are mostly not very satisfied about this mechanism and administrators like this mechanism because the more complex a password is the less a brute-force attack will succeed. Users mostly do not understand why these mechanism are necessary and so they try to avoid using complex passwords. [7]
Next to these complex passwords many users have a lot of systems that they use. Let's face a normal internet user and the user names he or she might have:
- BIOS password
- User name and password:
- Computer password (log on on operating system)
- Ebay
- Amazon
- MySpace
- Wikipedia
This list indicates that there are a lot more user names and passwords for one user. For each online-shop the user will need user name and password again. Every system that the user wants to use will ask for a user name and password. As the reader can see this list is far away from being complete. A lot of other systems can be named here with a similar functionality.
Web applications
Web applications (also called: Webbased systems) describe software that is accessible via the Internet and via browser software. The Internet is not necessarily needed so that also Intranet based solution are called web applications. The applications mostly make use of HTML-, JavaScript and PHP-/ASP-Technology. Standard examples of web applications are webmail, auctions, online-shops, social communities.
Examples for webbased systems with user name and password authentication:
- Shops
- Amazon
- Bol
- Buch.de
- Auctions
- Ebay
- Marktplaats
- Upload Portals
- Rapidshare
- Uploaded.to
- Megaupload.com
- Internet radios
- RauteMusik.FM
- Techno4ever.net
- Clubs
- Alpha Music Parc
- Other Systems
- PayPal
- Social Communities
- MySpace
- Hyves
- Mein/StudiVZ
- SchuelerVZ
- Google (for email and other services next to the search engine)
- YouTube
- MobileMe
Especially the social community services offer the possibility to offer plug-ins for each often used service. For example a post on twitter can be made available on Twitter, Hyves, StudiVZ and MySpace. So one post will be published on several systems.
The list also shows sites where the user without login only gets an impression of what is possible. The full functionality is then only available to users that are registered.
Software
Next to web applications also software exists where users have to authenticate at the start up. Examples of these kind of software are ERP systems mostly used in organizations. Within these ERP systems important documents will be created like invoices and some organizations require that the writer of the document is traceable.
Next to that also online banking software requires some kind of authentication. Mostly installed software uses a smart-card reader or a similar device for authentication together with a PIN (personal identification number).
Hardware
At least there is also hardware that requires some kind of authentication. There are several examples available like door locks based on key cards with access codes or car keys with a driver identification. Also a computer with a BIOS password has some kind of authentication because knowing the password leads to the assumption that the user is allowed to use the computer. Every Sim card for a cell phone has some kind of hardware protection because if one wants to use the card he needs to know the PIN code. Also this procedure is some kind of authentication. Users tend to use some kind of known numbers for the PIN code, like birthdays or the same code as used for the credit card.
Improvement of usability
In the future more and more systems will make use of user name and password authentication. Most services will be offered through the Internet and as of today the largest amount of authentications are needed on websites. Therefore a new approach is needed for improved usability. At this moment browsers like FireFox and Internet Explorer try to solve the usability issue by saving all user names and passwords on the local computer. When the user now switches the computer or uses another device all passwords will not be available to the user. The user has to remember all passwords or has to find another way to use a password system on different systems. A certain USB stick software makes it possible to install programs on a USB stick. Then the user is able to save the passwords on the USB stick but if the system does not support the USB stick, the user will have the same problem again. He will again be looking for his access information for certain services.
Man in the middle approach
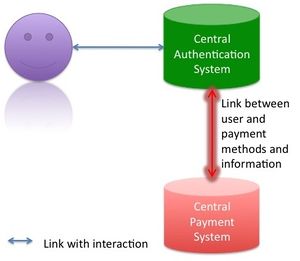
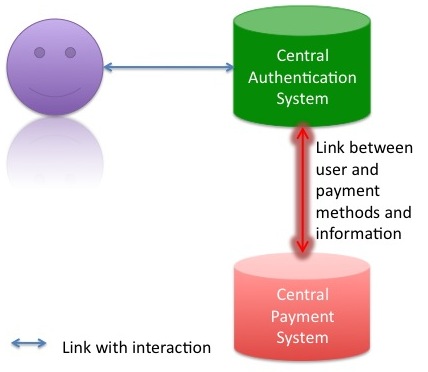
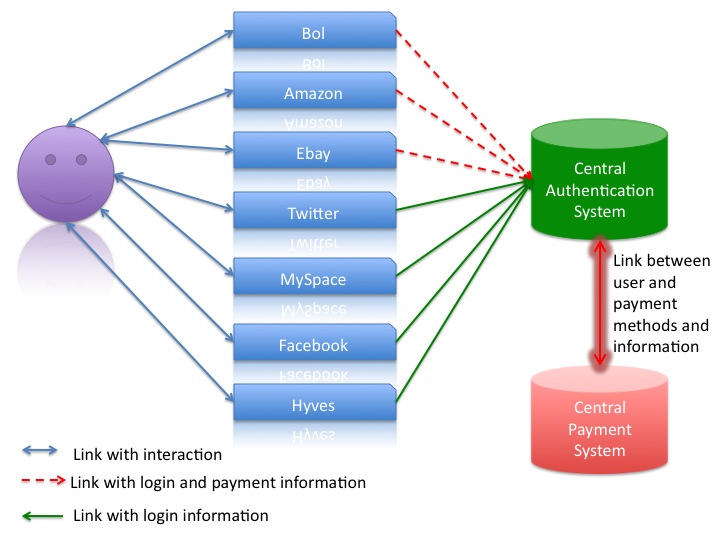
Since several years a secure HTTP connection is possible via HTTPS. This protocol includes certain standard certificates. These certificates are authorized and certain standard browsers trust these certificates. A similar way can be chosen for the authentication of users and the administration of user information. In another approach the client will have no responsibility and a central system will be the heart of a new authentication mechanism with the goal of more satisfied users. At the central system the user will be able to register himself. So he only needs to run through one registration process. The registration process includes the creation of a profile and the profile information can later be used for the services that the user wants to use. The process is shown below.
If the user know wants to use a service like Amazon or Facebook he can go to these services and register. The registration process will be the following:
- Go to the central server
- Login with usal credentials
- Add Amazon to your services you want to use
- Central server will send profile information to Amazon
- Amazon will create a profile
- Amazon will contact user that profile has been created
- Go to Amazon and enjoy buying
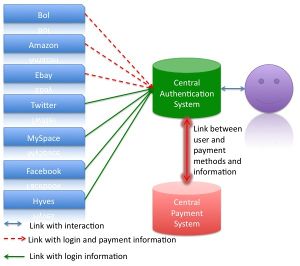
This process will be the same for other services like shown in the graph below.
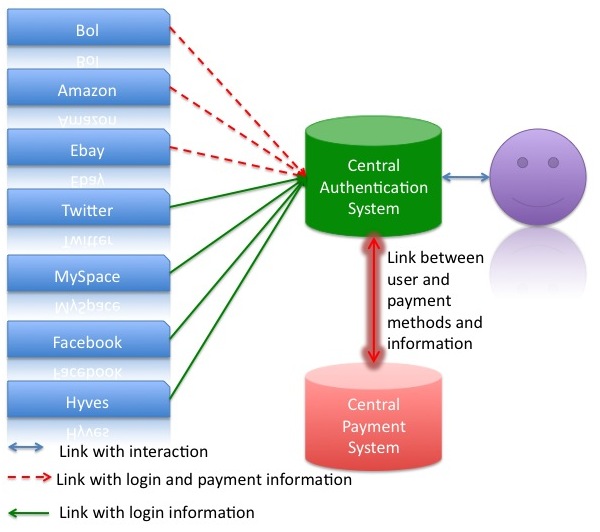
For a service like Amazon the payment information is necessary. The information will also be stored on the central server. In the graph this information is separated because certain services do not need that information. These services can mostly be used without payment. The graph shows the difference between these services with the different kinds of lines used.
Central approach
In a more central approach the user would only log on on one system. Therefore the system must been able to gain access to the services the users want to use. This means the service has to gain access to Amazon, Ebay, etc.. On the other side this would mean that the central system can send one query to more than one system. In a pragmatic example a query for a certain product can e.g. run on Amazon and on eBay and the user sees all results.
At this moment it is not clear whether Amazon or eBay have to get the log on information from the user. Sure is that they will need an invoice address and further information about the order. This information has to be transferred from the central system to the sub-system.
For the user the approach is very simple because he will most likely only use one system, but has also the possibility to use all connected services. The interface would be the same and the user would have one user name and password. The usage would be centralized and the other services would be connected with plug-ins to the central system.
Existing systems
Ebay
In some way the central approach almost exists. Ebay is a very classic one where buyers and sellers meet on a market. Ebay is the (let's call it) gateway for both parties. Ebay is responsible for authentication and when both parties are authenticated Ebay will establish a connection between both. The connection can be a buy and by using systems like prepay or paypal the parties do not have to share essential information. The buyer get the bank account information of the seller or the paypal account name where the buyer can transfer the money to. That is enough for a secure buying plattform. Please not that Ebay is a bidding plattform.
Yatego
Another system is Yatego where buyers can put their products on. Here the buyer will find a lot of different sellers for the same product. If the buyer searches for one product he will get a list of this product but offered by different sellers, different prices, different shipment costs. The buyer will only see one crate even if he buys products at different sellers. The order will be sent to Yatego and Yatego will send the information of the buyer to the seller. The seller then defines the payment methods and the buyer has to pay. The product will be shipped directly to the buyer, not via Yatego.
Amazon
Very similar is Amazon. Amazon has its own shop but also other sellers can participate in the program. The process is very similar to the process of Yatego with one difference: Amazon is itself a seller.
External Links
Future Work
A central system has always the issue of security. Especially an online system has to be secured very well because a lot of bad guys will try to gain access to the account data of the users. Therefore some research has to be done how such a central system can be secured and how will the implemented counter measures influence the usability of the system. The security might be comparable to central systems like GlobalTrust or VeriSign who are responsible for the distribution of certificates. The certificates make it possible that users can connect to "trusted" servers by using a signed certificate. The certificate would indicate that the server is trustful. A similar system might be an option for a central usage system for the users. They can trust the new central server which has secured connections with certain services. The centralization of GlobalTrust, etc. indicates that central system are trustworthy and can be used. Another issue is the design and architecture of the new system. The new central system should mainly be focused on usability for the users. How should the elements be placed, which colors should be used and which information should be available on the central system. Next to this the whole implementation should be planned. Maybe a central website is enough to provide the users with enough usability, but maybe a local installation would make things easier. Also the usage of smart phones should be taken into account. Some smart phones require special development and how many users would gain something from that particular development.
Used articles
A proposed index of usability: a method for comparing the relative usability of different software systems
Abstract
Usability is becoming a more and more important software criterion, but the present usability measurement methods are either difficult to apply, or overly dependent upon evaluators' expertise. Based on human information processing theory, this study identified eight human factors considerations which are relevant to software usability. These considerations as well as the three stages of human information processing theory formed the framework from which our Purdue Usability Testing Questionnaire (PUTQ) is derived. An experiment was conducted to test the validity of PUTQ. The experiment result showd high correlation between PUTQ and the Questionannaire for User Interaction Satifaction (QUIS version 5.5). In addition, PUTQ detected the differences in user performance between two experimental interface systems, but QUIS faild to do so.
Relevance
The troupe with login: on usability and computer security in ubiquitous computing
Abstract
Abstract Logging in by typing usernames and passwords is by far the most common way to access modern computer systems. However, such contemporary user authentication mechanisms are inappropriate in a ubiquitous computing environment, where users constantly are accessing a wide range of different devices. This paper introduces new concepts for user authentication in ubiquitous computing, such as the notion of proximity-based user authentication and silent login. The design of these new mechanisms is part of the design of a ubiquitous computing infrastructure for hospitals, which is grounded in field studies of medical work in hospitals. The paper reports from field studies of clinicians using an electronic patient record (EPR) and describes severe usability problems associated with its login procedures. The EPRís login mechanisms do not recognize the nature of medical work as being nomadic, interrupted, and cooperative around sharing common material. The consequence is that login is circumvented and security is jeopardized.
Relevance
Web Site Usability, Design and Performance Metrics
Abstract
Web sites provide the key interface for consumer use of the Internet. This research reports on a series of three studies that develop and validate Web site usability, design and performance metrics, including download delay, navigability, site content, interactivity, and responsiveness. The performance metric that was developed includes the sub constructs user satisfaction, the likelihood of return, and the frequency of use. Data was collected in 1997, 1999, and 2000 from corporate Web sites via three methods, namely, a jury, third-party ratings, and a software agent. Significant associations between Web site design elements and Web site performance indicate that the constructs demonstrate good homological validity. Together, the three studies provide a set of measure with acceptable validity and reliability. The findings also suggest lack of significant common methods biases across the jury-collected data, third-party data, and agent-collected data. Results suggest that Web site success is a first-order construct. Moreover, Web site success is significantly associated with Web site download delay (speed of access and display rate within the Web site), navigation (organization, arrangement, layout and sequencing), content (amount and variety of product information), interactivity (customization and interactivity), and responsiveness (feedback options and FAQs).
Relevance
This article goes into detail about the usability of web sites and the navigation on web sites. This is very important for the user since authentication can be a part of navigation.
References
- ↑ Han X. Lin, Yee-Yin Choong and GAVRI EL SALVENDY, A proposed index of usability: a method for comparing the relative usability of different software systems, BEHAVIOUR & INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY, 1997, VOL. 16, NO . 4/5, 267 - 278
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google_Chrome_OS
- ↑ Jonathan W. Palmer, Web Site Usability, Design and Performance Metrics, Information Systems Research: Jun 2002; 13, 2, pg 151
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Usability
- ↑ http://www.pc-boeken.nl/usability/woordenlijst/
- ↑ Jakob E. Bardram, The trouble with login: on usability and computer security in ubiquitous computing, Pers Ubiquit Comput (2005) 9: 357–367, Published online: 23 July 2005, Springer-Verlag London Limited 2005
- ↑ Jakob E. Bardram, The trouble with login: on usability and computer security in ubiquitous computing, Pers Ubiquit Comput (2005) 9: 357–367, Published online: 23 July 2005, Springer-Verlag London Limited 2005